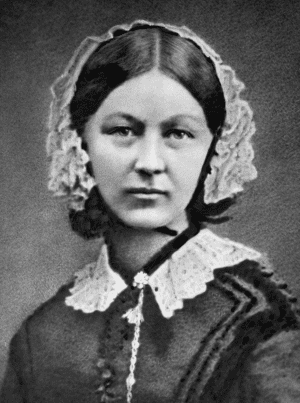Keystage history
Benin – KQ6 – Should the Benin Bronzes be returned? SMART TASK
This lesson is guaranteed to provoke a lively debate. Armed with all the contextual knowledge they need, and stimulated by…
Read MoreLinking your early civilizations at KS2
There is a real and present danger in KS2 of failing to make links between topics. If we are not…
Read MoreWizards and scientists:changing views of Stonehenge. History as interpretations and a constant conversation between past and present
One of the harder parts of teaching history at Ks2 is to explain to pupils that history is a construct,…
Read MoreUsing fiction in KS2 history. What can we read with our pupils during our Ancient Egypt topic?
For many years I have been advocating the use of fiction at KS2 to help pupils to realise the importance…
Read MoreBanality of OFSTED’s KS1 judgements in history. They don’t know what they are talking about. Stick to your guns.
Sometimes you just have to say it. What on earth do they expect? reading through a number of OFSTED reports…
Read MoreMedieval Britain: The Crusades
Great lesson on the reasons for the First Crusade which uses a Zone of Relevance activity to show students how…
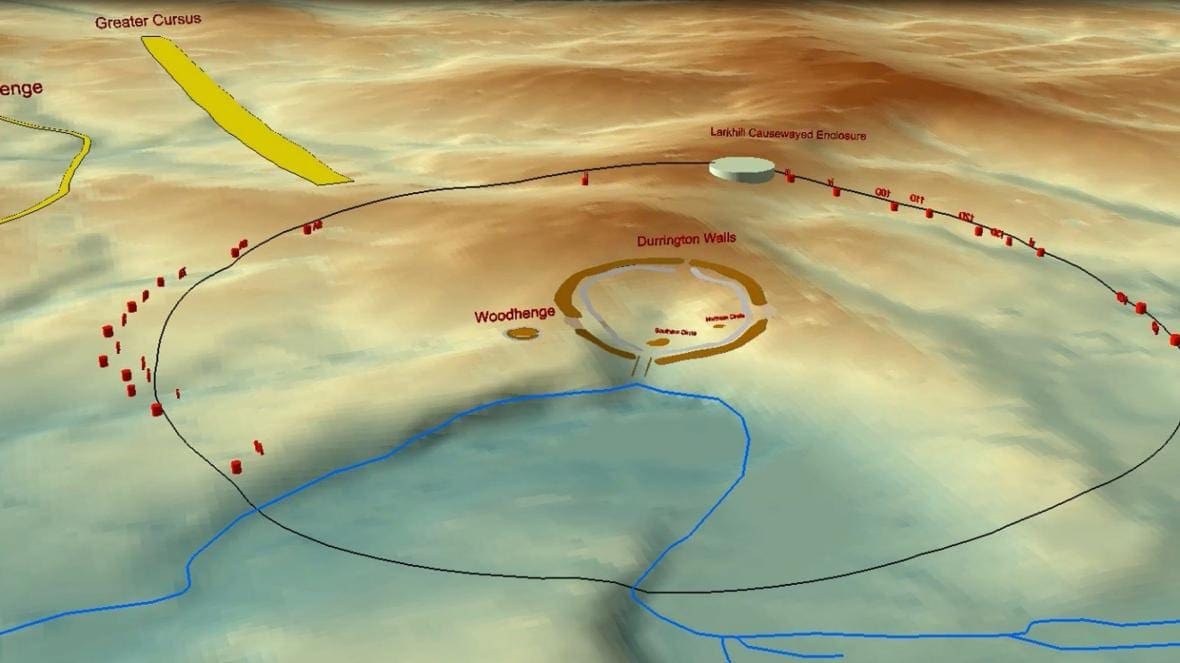
Read MoreIs this another find to help us understand Stonehenge?
Yesterday’s more interesting news centred on a newly-published report on the finds at Durrington Wells on Salisbury Plain. As the…
Read MoreOutstanding Lessons: Key Stage 1
If you have ever searched the internet for inspiration for your history sessions you will know how frustrating it can…
Read MoreThinking about evidence at KS2. How do we know what happened in Saxons times?
Where does our knowledge of the Anglo-Saxons come from? It is important that we ask the recurring question “How do…
Read MoreThe importance of getting your key questions right in your KS2 history planning
Scanning through a number of KS2 history websites recently, I realised just how narrow a view of history was being…
Read MoreHow much do you need to talk about chronology when studying Ancient Egypt?
This is a question that has concerned many primary teachers for a long time. I have sat in the back…
Read MoreInteresting resources on Florence Nightingale and Mary Seacole
Great resource on Mary Seacole https://www.mylearning.org/stories/mary-seacole/199? There are three games and an interactive glossary, each one narrated by Mary Seacole. The…
Read MoreImproving diversity in your KS2 history curriculum
Amid the current state of heightened racial tension across Britain and the USA, I thought it might be a good…
Read MoreGetting your enquiry questions right for your history topics at KS1
Getting your enquiry questions right at KS1 On the Historical Association website is a scheme of work on George Stephenson…
Read MoreAssessment for Learning: 5 core strategies that work
Helps teachers to collect information about pupils’ achievement in order to adjust teaching to meet pupils’ learning needs more fully,…
Read MoreA six step approach to history lessons
Step 1: Teacher motivates pupils to want to learn and scopes the enquiry Hooking them in: eg. with a slow…
Read More10 questions which we should ask when planning historical enquiries at KS2
Subscribers only: You must be logged in to view this content in full. Please Login or register
Read MoreProgression in historical interpretations at Key Stage 2 – How the past is represented and interpreted in different ways, and to give reasons for this
Beginning of Key Stage Children can identify differences between versions of the same event e.g. the video gives a different…
Read MoreWhat are deep dive OFSTED reports saying about history within the EIF 2019 Framework
I thought I would publish all the OFSTED deep dive reports I can find which illuminate what schools should be…
Read MoreWhat inspectors report on in deep dive history inspections: a recent example with my commentary from 2020
What the inspectors said Commentary Pupils in your school thoroughly enjoy learning history. They like the enquiry-based approach you…
Read MoreMeeting OFSTED’s criteria for a good history curriculum at KS1 and 2 during extended transition period
Now that schools have an extra year’s grace from OFSTED to refine their curriculum that is being worked on, it…
Read MoreUsing timelines in history at Key Stage 2
Timelines in school may be individual timelines or made collaboratively with different groups working on separate theme within a study…
Read MoreThinking historically: ‘learning to’..as well as ‘learning about’
While so many of you are locked down, it seems a good time to remind you of the key features…
Read MoreImproving history in your primary school: a short cameo of a success story
So what does effective leadership of primary history look like? A case study When Lara took over as history subject…
Read MoreFlorence Nightingale and her legacy – 200 years since her birth, on 12 May 1820
Historians have praised Florence Nightingale on the 200th anniversary of her birth, and said her legacy has “never been more…
Read MoreUsing quadrants to answers exam questions at GCSE and A level
Sometimes the simplest ideas are the best. Faced with an exam question such as How far do you agree with…
Read MoreGCSE history: Answering the question set , not the one they would prefer to answer.
Many of you teaching GCSE will be familiar with the issue. Your students answer the question they think the examiner…
Read MoreTeaching Toys to Key Stage 1
Toys is an obvious topic to select for infants. Not only is it appealing , at least initially, it is…
Read MoreKS1 Medium term planner: Toys through time (Term 1 or 2 of Y1)
This is one of the earliest topics to be taught at EYFS/KS1 following on from Myself. As we know this…
Read MoreHistorical Association survey of secondary history provision 2019- few surprises and some disappointing statistics
Last week saw the publication of the annual survey into secondary history produced by the Historical Association. Obviously reflecting the…
Read MoreToys – KQ1 – What are our toys like today?
Because the topic is aimed at children beginning key stage 1, it is a good idea to spend more time…
Read MoreKey ideas in primary history
When we are teaching 11 subjects it is often difficult to catch the essence of each. If we’re not careful…
Read MoreToys – KQ2 – What are other people’s toys like?
This session comprises two very simple tasks: matching objects to the young children who would usually play with them, followed…
Read MoreGreat learning activity: Prove it! See examples for Scott of the Antarctic, Man on the Moon, Tudor theatre, Grace Darling, Louis Braille
One of the most effective learning activities which you will find in a small number of the outstanding lessons is…
Read MoreRemembering VE Day
In these difficult times when schools are not in session it will not be possible to commemorate the ending of…
Read MoreCreating your own timelines at KS2: one school’s recent find.
Charley Chanter of HertfordHeath primary school has just brought this Timeline making package to my attention He wrote:.I have been…
Read MoreRotten apple or …. How should we portray Dyer’s motivation in the Amritsar massacre?
This enquiry asks students to look critically at the depiction of the massacre in the film Gandhi as a way…
Read MoreAt last a way forward with KS2 assessment for history that will work for my school
Even though we will have had the National Curriculum for history ( albeit in different guises) for nearly 30 years,…
Read MoreHow to assess pupils’ progress in KS2 history. At last the answer that not only works but will work for you too.
Even though we will have had the National Curriculum for history ( albeit in different guises) for nearly 30 years,…
Read MoreTeaching American West at Key Stage 4
Schools have been teaching the American West as part of the SHP course for over 30 years. I introduced it…
Read MoreTeaching the History of Medicine
As you all know, the trick with teaching this course is to marry a strong contextual knowledge with an understanding…
Read MoreWe learn by being excited not by being told; abiding principle of Keystage history
I get a lot of enquiries about Keystage history, largely from teachers who want to know what to expect from…
Read MoreAre you teaching the right things about Mary Seacole to your children? 10 things to be sure to teach
Are you teaching the right things about Mary Seacole to your children? 10 things to be sure to teach: 1….
Read MoreMore thoughts on primary history OFSTED deep dives
Recently Matthew Purves, the Deputy Director for Schools, set out OFSTED latest thinking on deep dives in primary schools. He…
Read MoreKS1 Medium term planner: The sinking of the Titanic Y2
This topic provides an exciting addition to the usual famous events taught at KS1. Not only is there a clear,…
Read MoreDid you know there were over 1000 Roman sites in England and Wales?
The numerous discoveries of Roman finds, often by private metal detectors, have revealed more than 1,000 Roman sites in England…
Read MoreTeaching about Roman villas at KS2- some new finds in Gloucestershire. Should the housing development now go ahead – arguments for and against?
Those of you teaching about Roman villas at KS2, maybe even using the outstanding lesson on this website, Is this…
Read MoreOFSTED using frighteningly slender evidence to judge history at KS1 and 2
According to today’s Guradian report an eight-year-old boy was meeting the Ofsted inspector for the first time. “What do you remember…
Read MoreWhat is history? – Key stage 2
In the classrooms of some non-specialist Key Stage 2 teachers, history is still presented as the story of the past….
Read MoreWhat would OFSTED say about history in your school? What needs to improve? A sample recent report gives an insight
After identifying a number of positive features of the history curriculum and history teaching the OFSTED inspector carrying out a…
Read More